
The recurrent isolate ( PA2428) was resistant to all drugs, including aminoglycosides, C/T, and CZA, except polymyxin B (Table 1). Four days after CAZ was discontinued, she developed a recurrent bloodstream infection due to P. Aztreonam 1 g intravenous (IV) every 8 hour (q8 h) was started with successful clearance after five days, and the patient was switched to CAZ 1 g IV q8 h for an additional 13 days.

aeruginosa (susceptible to aztreonam, CAZ, C/T, ceftazidime-avibactam (CZA), and polymyxin B (isolate PA2312)). During her hospitalization, the patient was found to be bacteremic with P. aeruginosa, which required prolonged courses of antibiotics with ceftazidime (CAZ), cefepime, meropenem, and amikacin. The patient had a history of polymicrobial bacteremia, including P. A 21-year-old African American female with a history of autoimmune hemolytic anemia (receiving prednisone 5 mg orally every day) presented with acute vascular necrosis of the right femoral head after a fall. We investigated the genetic basis of C/T resistance by whole genome sequencing, and the contribution of AmpC β-lactamase activity to the resistance phenotype was evaluated. aeruginosa before (susceptible) and after (resistant) treatment with β-lactams were recovered. In this work, 2 patients who developed C/T resistance during therapy are described and their isolates of MDR P. Previous reports have suggested that the mechanism of C/T resistance is associated with changes in the Ambler class C β-lactamase AmpC. Unfortunately, resistance to C/T compromises the effectiveness of this antibiotic. Indeed, many reports have confirmed the success of C/T to combat these organisms. The new cephalosporin/ β-lactamase inhibitor combination ceftolozane/tazobactam (C/T) has provided a viable alternative for treatment of infections due to MDR P. The rise of multidrug-resistant (MDR) Pseudomonas aeruginosa threatens the use of available antibiotics, including carbapenems.
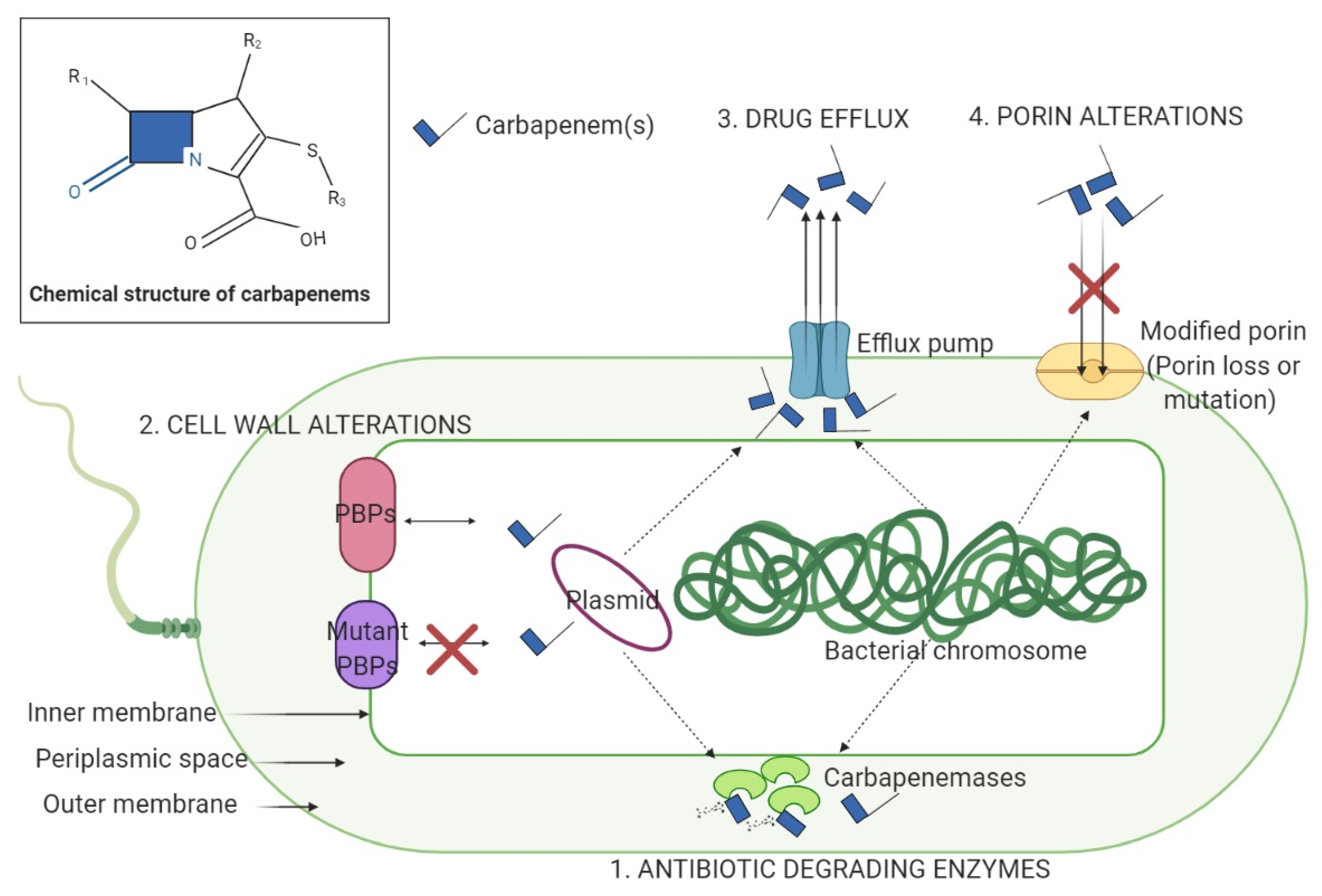
aeruginosa is associated with changes in AmpC however, the apparent loss of β-lactamase activity in AmpC∆7 suggests that non-AmpC mechanisms could play an important role in resistance to β-lactam/ β-lactamase inhibitor combinations. Resistance to ceftolozane/tazobactam in P. On the other hand, the deletion of 7 amino acids in the Ω-loop of AmpC did not display enhanced β-lactamase activity. Phenotypic assays showed that ceftolozane/tazobactam resistance in the strain with AmpC V213A variant was associated with increased β-lactamase hydrolysis activity. Whole genome sequencing identified mutations in AmpC including the mutation (V213A) and a deletion of 7 amino acids (P210–G216) in the Ω-loop. The genetic basis of ceftolozane/tazobactam resistance was evaluated, and β-lactam-resistant mechanisms were assessed by phenotypic assays. aeruginosa were isolated from 2 patients after exposure to β-lactams. Two pairs of ceftolozane/tazobactam susceptible/resistant P.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
